The information in this section is not intended for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In the event of pain or other worsening of the condition, diagnostic tests should only be performed by the attending physician. In order to make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor.
What injuries are possible to the knee?
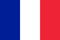
- United,
- the ends of the femur and tibia,
- muscle,
- vessel,
- nerve
- ligament,
- patella,
- meniscus,
- joint capsule.
Knee pain can be caused by damage to the femur and tibia and nearby muscles.
Knee pain due to injury
- bruised knee- Fairly weak and very frequent damage. With it, the knee will swell and become red, and the joint temperature may increase slightly. If bruising occurs, a knee massage may be needed;
- Ligament ruptureThis condition occurs when the leg or thigh twists too much in an unnatural direction. A complete ligament rupture can cause severe pain and joint hypermobility;
- meniscus tearIt can be caused by high loads, an unnatural position, a blow to the leg, or a twisted tibia. This is a common and difficult-to-diagnose injury that interferes with normal movement of the leg;
- Broken knee, leg, or hipThis, combined with soft tissue damage, results in excruciating pain, hypermobility, and knee deformity.
What joint conditions cause pain?
- arthritis— Joint inflammation, which can occur after injury, infection, or metabolic problems;
- Bursitis- Inflammation of the joint capsule, causing severe discomfort when trying to move the joint;
- existperiarthritisInflammation of the tendons, muscles, and ligaments around the knee joint. Pain occurs when the load on the bent leg is increased, such as when descending stairs;
- rickets— Gradually destroys the cartilage surrounding joints and softens friction and impact;
- tumorThey can compress blood vessels and deform the joint capsule, causing pain and limiting mobility;
- existosteoporosisCalcium is gradually washed away from bones and joints, and the tissues become brittle. The disease is associated with pain and an increased risk of injury;
- osteomyelitis- Inflammation of bone tissue. Significant swelling of the affected area, increased body temperature, and severe acute pain;
- diseaseIllnesses of various natures, such as influenza and tuberculosis, may cause complications due to infection entering the joint capsule. In these conditions, increased body temperature, weakness, and pain occur simultaneously in multiple joints.
Knee pain due to nerve damage
- neuritis- Neuroinflammation in one or more areas. With it, patients experience throbbing pain and loss of sensitivity, their mobility may decrease, and their legs begin to shrink involuntarily at the knees;
- pinch nerve- Common consequences of inflammation, tumors and injury. Due to physical pressure on the nerve roots of the knee joint, symptoms such as burning pain, numbness, difficulty moving, and even paralysis may occur.
Can the cause of knee pain be determined from the symptoms?
- If you feel numbness or tingling in addition to pain,nerve damage;
- Increased temperature and swelling of the knee -signs of inflammation;
- General weakness, fever and poor health -Post-disease joint disease;
- Pain can occur not only in the knees but also in other joints, such as shoulders or fingers: it may look likeosteoporosis, and the consequencesinfectious disease;
- The joints will hurt violently when trying to bend or straighten the legs, and they will be very weak at rest.Bursitis or advanced rickets;
- Impaired range of motion but no loss of sensitivityJoint destruction, tumors or arthritis;
- Broken bones, dislocations, and bruises are preceded by a blow or fall that you can't possibly ignore. inJoint dislocation, ligament and meniscal injuriesWith knee hypermobility.